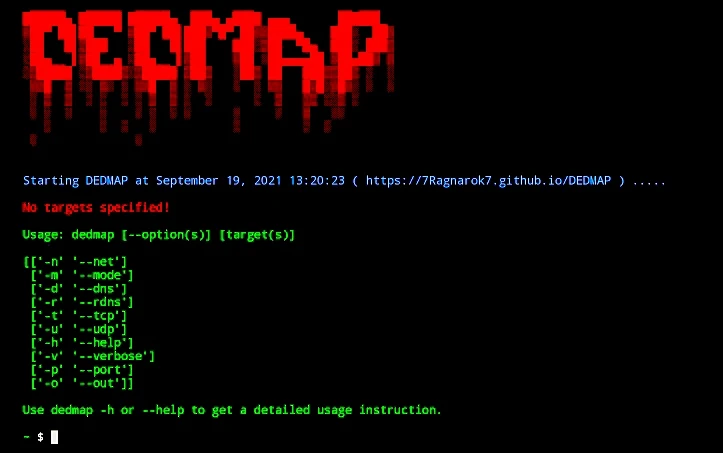
DEDMAP is a free and open-source utility that can be found on GitHub. It functions as a scanner, scanning domains and websites. DEDMAP is a robust, cross-platform scanning utility. DEDMAP is a port scanning programme that is very similar to nmap.
It is written in the bash programming language. To use this tool properly, you must have the bash language installed on your Kali Linux system. DEDMAP separates all UDP and TCP protocols into ports ranging from 0 to 65535. These ports are further classified as sub-ranges.
- System or reserved ports: from 0 to 1023
- User or registered ports: from 1024 to 49151
- Dynamic or private ports: from 49151 to 65535
DEDMAP tries to scan a target IP or range of IP’s and find services that are running and listening on some ports. DEDMAP can also scan a range of hosts to find live hosts.
Requirements
Installation
Step 1: Run the command below to download the tool from GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/7Ragnarok7/DEDMAP.gitStep 2: To install the tool, run the following command.
./install.shThe tool has been successfully downloaded and installed. Now we’ll look at some instances of how to use the tool.
Usage :-
$ dedmap [–option(s)] [target(s)]
Example 1: Scanning a domain using the DEDMAP tool.
dedmap <domain>


This is how scanning with dedmap is done.
Example 2: Using the dedmap tool to scan various websites.
dedmap -d google.com yahoo.com facebook.com localhost- If no options are provided, the tool will perform a TCP scan by default.
- You must include the `-t` option if you use any other options like `-p`, `-v`, or `-n`.
- If no ports are specified, the tool will automatically scan the top 100 most commonly used ports by default.
- Long Options (–) have more priority.
Options :-
- -h, –help show this help message and exit
- -b, –black turn on dark-web mode
- -s, –silent run in silent mode (remove the dedmap banner)
- -v, –verbose run in verbose mode
- -d, –dns performs a DNS lookup
- -r, –rdns performs a reverse dns lookup
- -p, –port<port(s)> only scan specified port(s)
Ex: -p 21; -p 21,22,23;-p top10; (scan top 10 commonly used ports)-p top100; (scan top 100 commonly used ports)-p top1000; (scan top 1000 commonly used ports)-p system; (scan system ports from 0 to 1023)-p user; (scan user ports from 1024 to 49151)-p private; (scan private ports from 49152 to 65535)-p all; (scan all ports from 0 to 65535)- -t, –tcp perform a TCP scan (default scan if NO OPTIONS are specified)
- -u, –udp perform a UDP scan (Doesn’t seems to work as of now using the socket in python)
- -n, –net perform a network scan
- -m, –mode<wan/lan> select the mode for network scan (default = wan)
Select lan mode(turbo mode) for better scanning speeds (upto 5x)It is recommended to use the turbo mode only on a lan networkas it might result in loss of accuracy in wan networksEx: -nm lan; -nm wan;- -o, –out saves the results in a file
Ex: -o report
Additional Notice :-
- The output file generated is a dedmap file. Cat/Print it to view it’s contents properly in a shell environment.
- This tool likely has many bugs because it is still in its early stages.
- This tool has not been tested in Windows yet and will not work most probably. Feel free to experiment.
Disclaimer :-
This tool is designed for educational and research purposes only. Use it only on systems or networks you own or with the owner’s permission. You are solely responsible for how you use this tool; I take no responsibility for your actions.
Also Read:
PhoneSploit Pro: Taking Phone Hacking to the Next Level
Cyberonix: A Valuable Tool for Cybersecurity Professionals